TEAM MEMBERS:
Names / Roles:
- (Leader)

- (Writer)

- (Research)

- (Research)

-
-
-

Overview
Below is a Map showing the types of forest:)
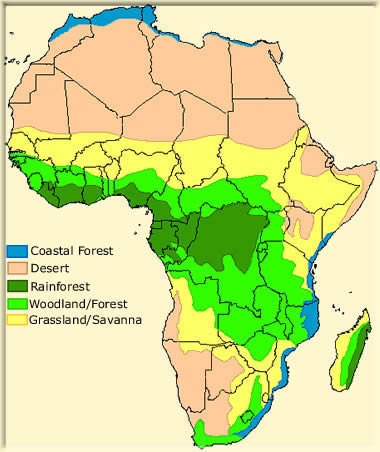
The African savanna are big areas of land that are covered in shrubs and grasses with a few trees. The temperature is between 60º and 75º all year. The seasons are still different, though. In the winter the savanna might get 4 inches of rain a month. In the hot, dry summer it is possible for absolutely no rain to fall. Most of the plants die in the summer, but the roots can live underground. The grass will grow back in the rains of winter. Many of the animals that live on the savanna are herd animals like gazelles, giraffes, and zebras that live on vegetation. There are many national parks in the savannas of Africa. People visit to go on safaris: trips to see the animals that live in the grasslands.
Countries: Kenya,Tanzania, Botswana, Mozambique, Zambia and Uganda.
It is tropical grassland, open or dotted with trees and rocky outcrops.



The most famous of the savanna people of Kenya and Tanzania are the Maasai tribe.
The Maasai people are just one of the many groups that live on the savanna of Africa. The Maasai tribe have lived in Africa for hundreds of years. They raise cattle. Families live together in groups of ten to twenty huts. Women build the houses and go for water. Sometimes they have to walk many miles to find water. Their main food is milk. They raise sheep and goats for meat.
As in other parts of Africa, people build their homes from materials they find on the land(branches,twigs,grass,mud)
African Savannah: The Ecosystem
Physical Factors
Temperature: between 60º and 75º all year .
No winter and summer seasons but there are two rainy seasons and two dry seasons a year. This varies according to latitude and may consist of one very short, wet season and one long, dry season. The changes between the wet and dry seasons are drastic and plants and animals must adapt to survive.

Water: Moves across Earth’s surface through organized networks of channels, known as rivers or streams. Although the flow of water may drainage basins. Watersheds play a critical role in the natural functioning of Earth’s environment. Physically, they integrate the surface water runoff into organized drainage nets. Economically, they play a critical role as sources of water, food, hydropower, recreational localities, and transportation routes. Ecologically, watersheds provide habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna. Individual rivers have different physical characteristics along their courses and create many of the landforms and landscapes within watersheds. Thus, the particular use of a river system is influenced by the nature of the individual river, the nature of the topography associated with the river, and where within the watershed one is located. African rivers often have unusual courses, waterfalls, and
rapids, and some lack deltas at the shore.
Salinity: A concentration (as in a solution) of salt
Mineral Salts:
Air:
Light:
PH: A measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, numerically equal to 7 for neutral solutions, increasing with increasing alkalinity and decreasing with increasing acidity. The pH scale commonly in use ranges from 0 to 14.
Seasonal Habitat Changes
- During the wet seasons,most of the water does not soak into the soil but collects or becomes runoff.
- Drinking water is abundant and humidity is high,reducing evaporation.
- During the dry seasons, only permanent water remains and low humidity makes water loss extreme.
- Many small animal species either die or they leave their eggs to hatch with the rains. Large animals must migrate, change their diet, or do without food and water.
- Fires occur during the dry seasons, encouraging re-growth of grasslands.
Plants
The savannah grassland consists of many species of grasses (Elephant Grass)

- Elephant grass is a tall grass that originally came from Africa in 1913.
- It grows in dense clumps of up to 10 feet tall.
- In the savannas of Africa it grows along lake beds and rivers where the soil is rich.
- Local farmers cut the grass for their animals, carrying it home in huge piles on their backs or on carts.
- Yellowish or purple in color,the stems are coarse and hairy, and about 1 inch thick near the base.
- The leaves are 2 to 3 feet long, pointed at the ends, and about 1 inch wide.
- The edges of the leaves are razor-sharp.
- This makes stands of elephant grass nearly impenetrable.
- Many bird species make their home in the stands.
Animals
Herbivores with species ranging from insects such as grasshoppers, to large ungulates such as zebra and giraffe.
HERBIVORES: Only eat plants.


CARNIVORES :Meat Eaters.


African Savannah: Diversity
The number of species of animals present from season to season varies as a result of the following factors:
1.Life-cycles – many invertebrates and amphibians, such as grasshoppers and frogs, lay eggs and then die at the beginning of the dry season. The eggs do not hatch until the next day which rains.
2.Migration – animals dependent on daily water such as zebra move
to areas with permanent water during the dry season. Migratory birds such as eagles and swallows arrive with the rains from North Africa and Europe to escape the northern winter.
The population size of any one species is influenced by several factors:
Water availability – Most species reproduce at the beginning of the rains but
carnivorous, aquatic birds reproduce when water is low and fishes are easy to catch.
Food availability – Infant mortality in big cats increases as food becomes scarce;
scavengers are more abundant when other animals are dying from starvation.
Fire – Both natural and man-made fires occur frequently, preventing the development of bush land but encouraging grasslands which generate well after fires.
Classification of Living Organisms
Producers- Plants,trees, shrubs and short grasses
Primary Consumers-zebras and elephants
Secondary Consumers- lions, tigers, cheetahs, hyenas.
Decomposers-Mushrooms, insects and micro-organisms.
Food Web
Food web means a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
Below is the an example of a food web and hope you can understand them:)


OPEN UP THIS WEBSITE NOW FOR A CLEARER VIEW!
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rONHTMkYu0I
This a food web presentation for YOU! CLICK!
Interrelationship in Ecosystem
Predator-prey relationship
Predator means animal that kills and eats other animal.
Prey means an animal hunted by another for food.
This a predator-prey relationship between a:
Lions- Gazalle
Lions-zebras
Hyenas-deer



Parasitism The characteristic behavior or mode of existence of a parasite or parasitic population. relation between organisms in which one lives as a parasite on another.
Mutualism An association between organisms of two different species in which each member benefits.]
Example of such mutuaism is the:
The ants hollows out th large torns of a plant for nests.

Useful Links
Include the links of websites you took information from.
For example:
Wild World @ nationalgeographic.com ( http://www.nationalgeographic.com/wildworld/terrestrial.html )


Comments (6)
nazrul_hadi_jamali@... said
at 11:47 am on Apr 4, 2009
Hi Group 1
nice logos for names , but please remember to publish the more important facts soon, the deadline is near!
2E1group1 said
at 10:09 pm on Apr 5, 2009
OK
2E1group1 said
at 6:42 pm on Apr 6, 2009
this web is lacking-.-
2E1group1 said
at 7:37 pm on Apr 6, 2009
Hey why cannot adjust the names?? Khairina's name is out of the position!!
2E1group1 said
at 9:24 pm on Apr 6, 2009
dONE!
2E1group1 said
at 11:02 pm on Apr 6, 2009
i cannot seem to do the thing properly.. web site like lacking.
You don't have permission to comment on this page.